Evaluation of PPP-RTK under ionospheric scintillation
-
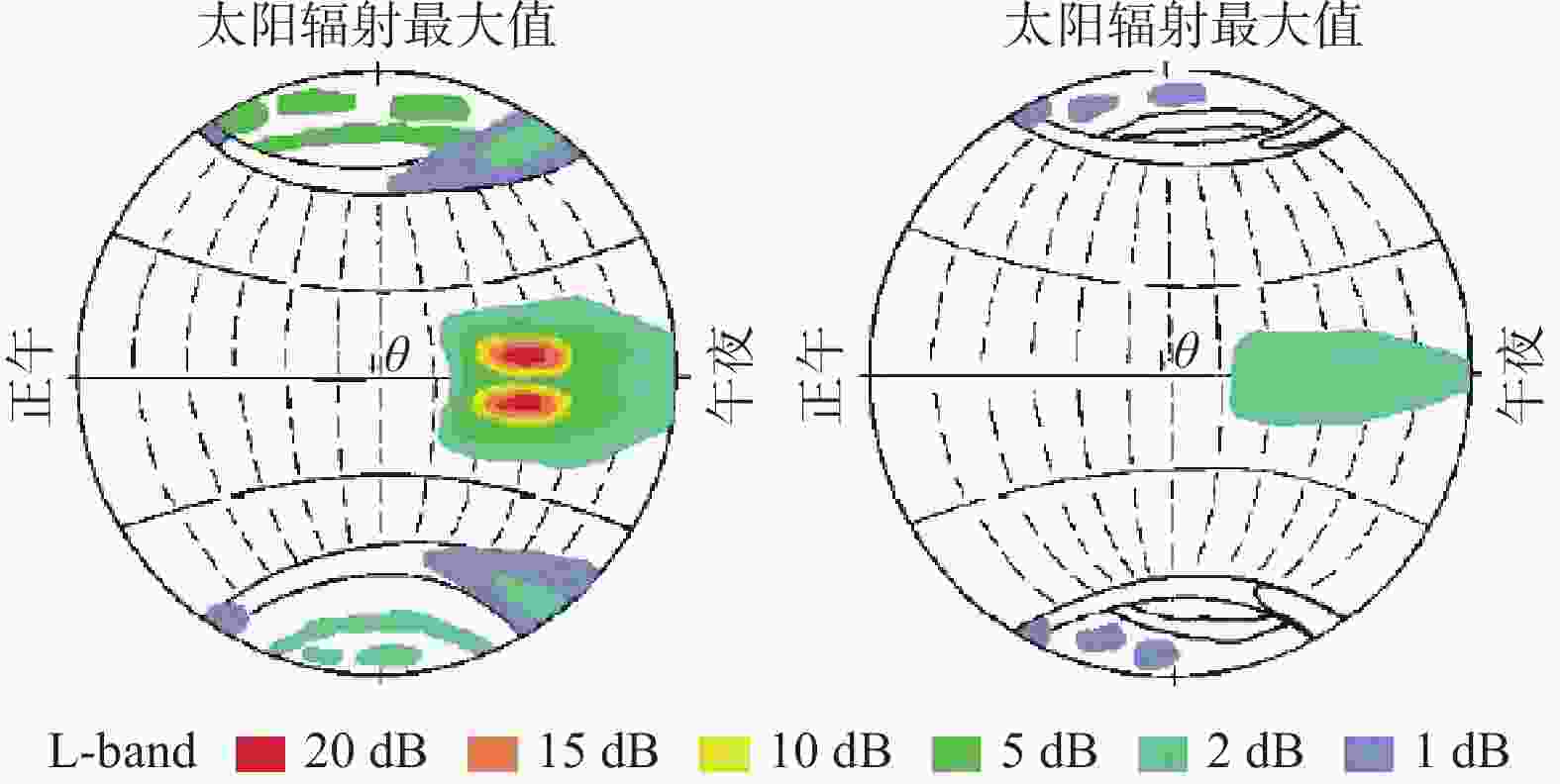
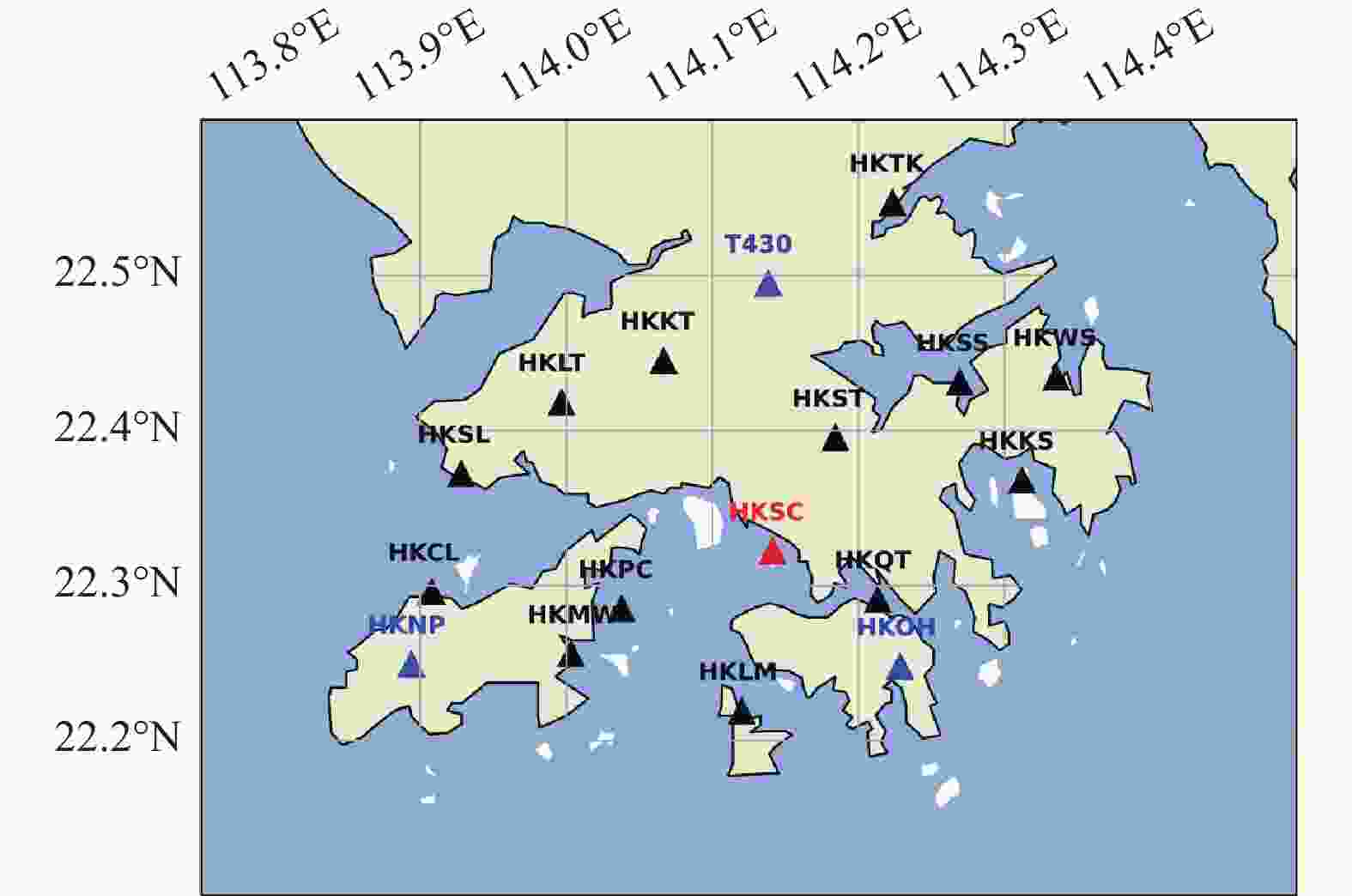
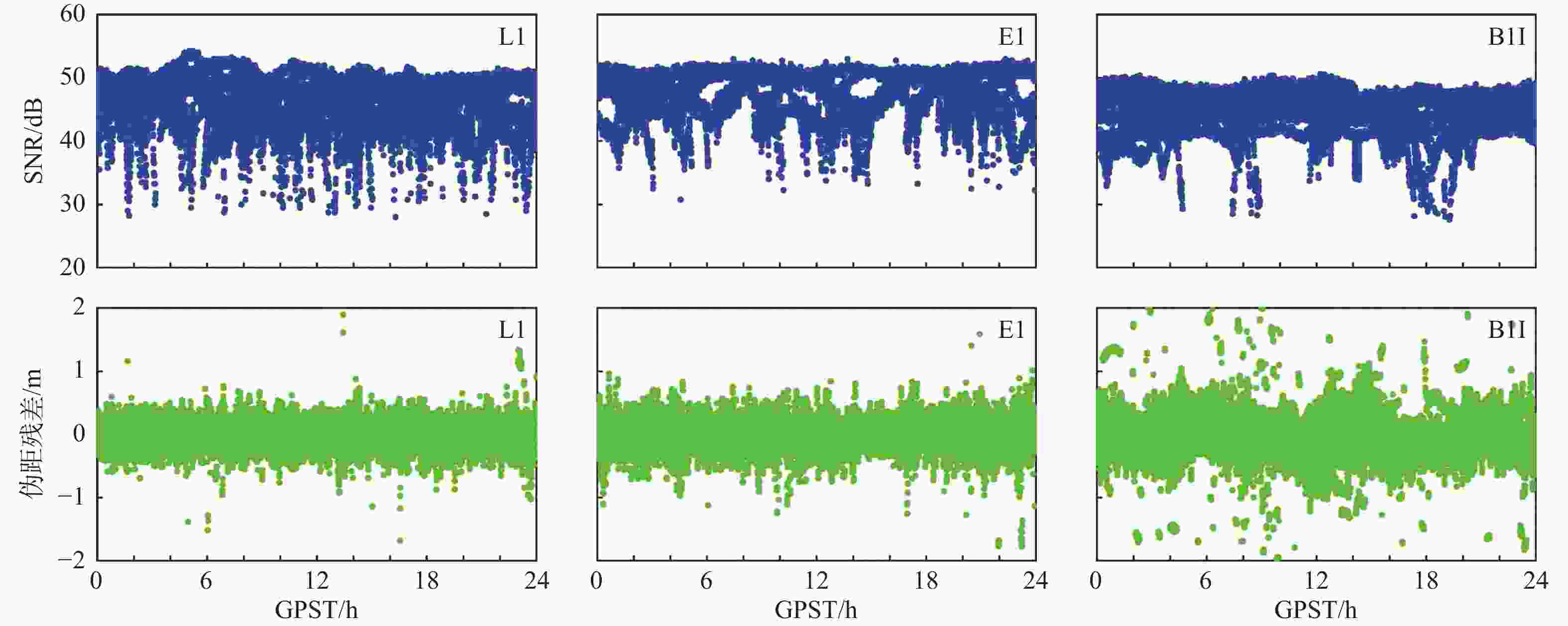
摘要: 精密单点定位(PPP)-实时动态(RTK)技术借助区域大气改正数可实现快速精密定位, 被认为是未来自动驾驶的首选技术. 然而,PPP-RTK在电离层闪烁环境下难以维持稳定可靠的定位,闪烁已成为PPP-RTK面临的重大挑战之一. 本文阐述了PPP-RTK模型和电离层闪烁特性,并基于香港卫星定位参考站网(SatRef)的实验数据从观测质量、周跳探测、大气产品和终端定位性能四个层面评估了电离层闪烁对PPP-RTK的影响. 结果表明:闪烁会降低观测质量,增大周跳误判的概率;GPS、Galileo、BDS三系统改正数精度分别降低了64.7%、64.0%、247.5%,改正数总数减少了4.5个;PPP-RTK定位误差较平静期增大了11.8倍,固定率下降了55.76%;GPS、Galileo、BDS三系统融合解算可大幅改善定位性能,较单GPS解算定位精度提升了93.06%,固定率提升了51.88%,但仍无法达到平静期的效果.
-
关键词:
- 电离层闪烁 /
- 精密单点定位(PPP)-实时动态(RTK) /
- 观测质量 /
- 周跳探测 /
- 大气改正数
Abstract: Precise point positioning real time kinematic (PPP-RTK) enables fast and precise positioning with the precise atmospheric corrections from the regional network, and it is regarded as the technology of choice for autonomous driving. However, PPP-RTK is hardly maintaining stable and reliable positioning result under ionospheric scintillation which has become one of the major challenges for PPP-RTK. In this contribution, the PPP-RTK model and ionospheric scintillation characteristics are introduced. The impact of ionospheric scintillation on PPP-RTK is analyzed in four aspects: observation quality, circumferential hop detection, atmospheric products and positioning performance based on the GNSS observations from the Hong Kong Satellite Positioning Reference Station Network. The results show that ionospheric scintillation reduces observation quality and increases the probability of wrong cycle slip detection. The accuracy of the corrections of GPS, Galileo, and BDS decreased by 64.7%, 64.0%, 247.5%, respectively, and the number of which decreased by 4.5. Finally, the positioning accuracy of PPP-RTK is increases by 11.8 times compared with the normal period, and the fixing percentage is reduced by 55.76%. The GEC mixed solution can significantly improve the positioning performance, of which the positioning accuracy in improved by 93.06% and the fixing percentage is increased by 51.88% compared with the GPS-only solution. -
表 1 PPP-RTK系统处理策略
项目 策略 GNSS系统 GPS、Galileo、BDS GNSS信号 GPS: L1, L2, L5
Galileo: E1, E5a, E5b, E5, E6
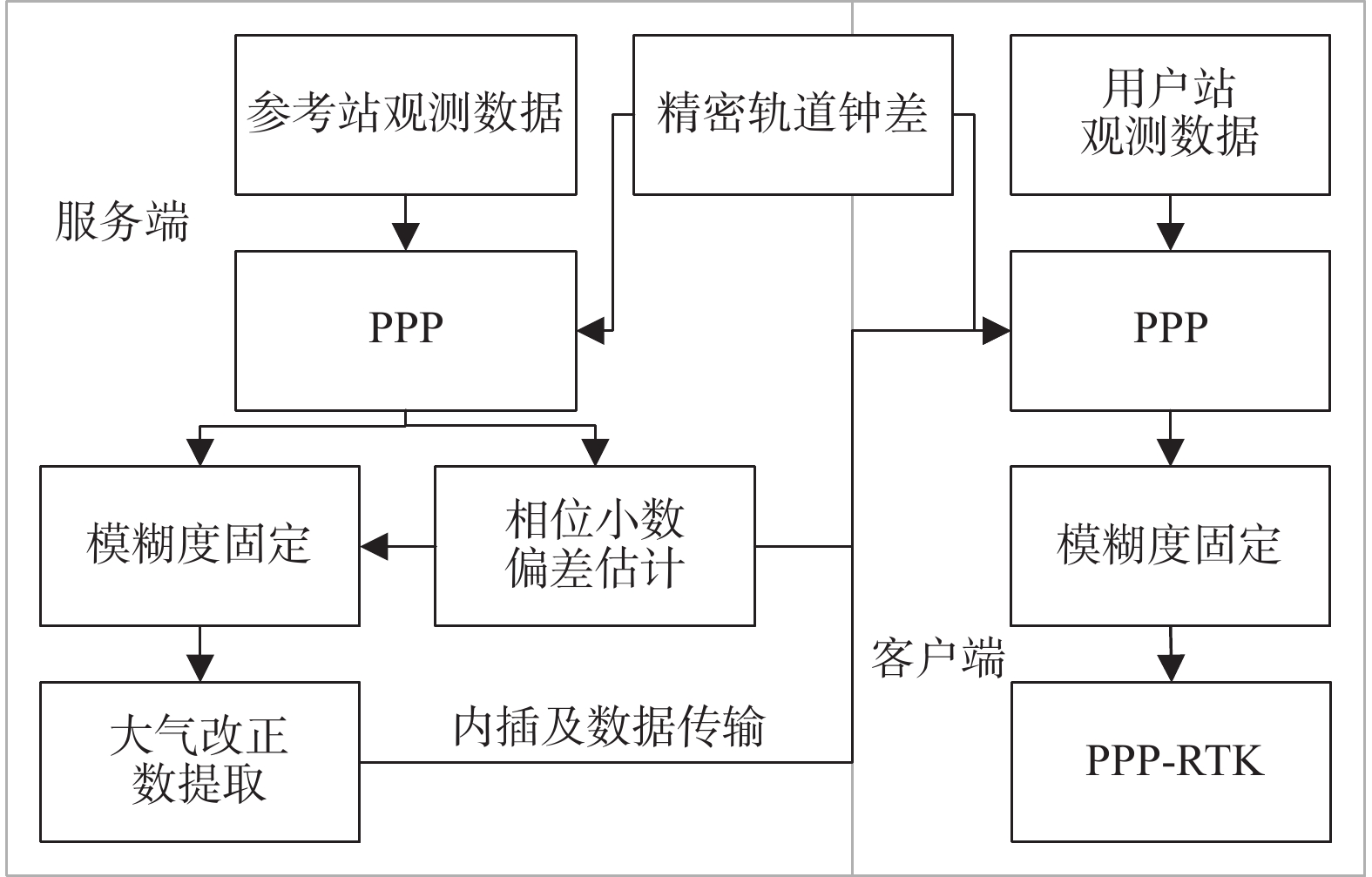
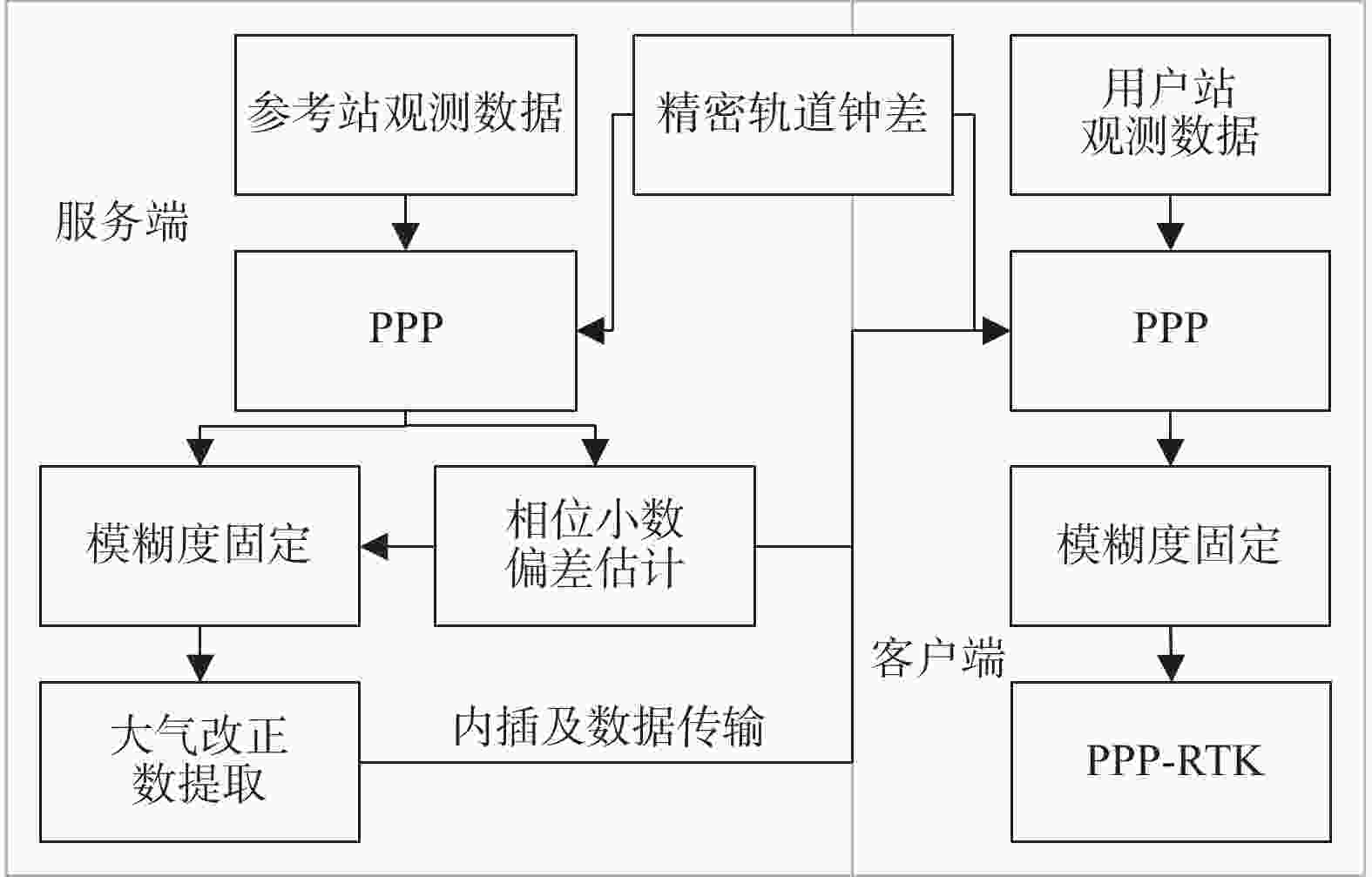
BDS: B1I, B2I, B3I组合模型 非差非组合 数据采样率 服务端:5 s 客户端:1 s 截至高度角 7° 最小卫星数 4 估计器 序贯最小二乘平差 观测值定权 高度角定权 相位缠绕 模型改正 电离层延迟 服务端:逐历元逐卫星进行WN估计
客户端:精密电离层产品改正对流层延迟 干分量:Saastamoinen模型+GMF投影函数
湿分量:服务端用随机游走过程估计;客户端用精密对流层产品改正卫星天线PCO/PCV igs14.atx 接收机天线PCO/PCV igs14.atx 接收机坐标 服务端:固定
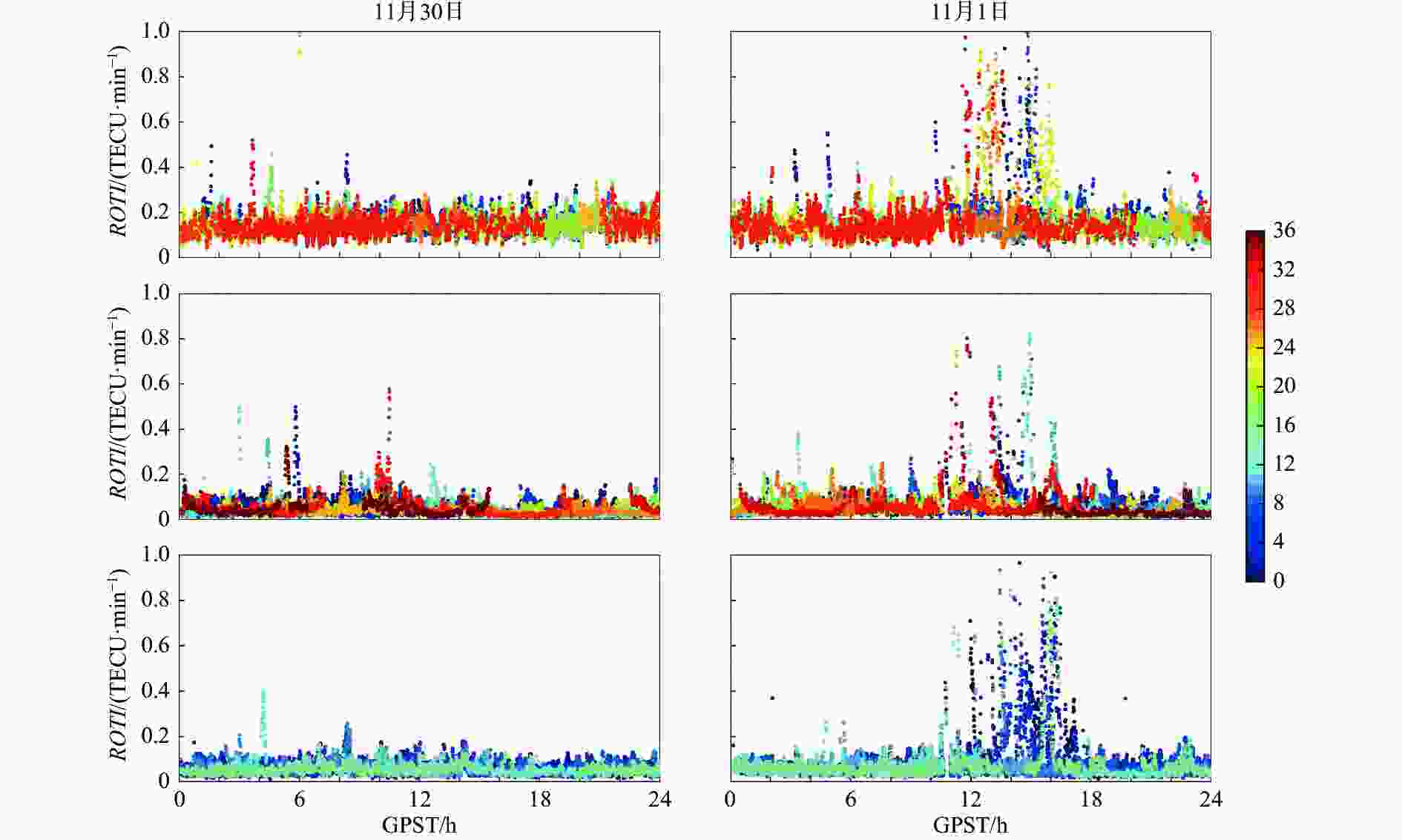
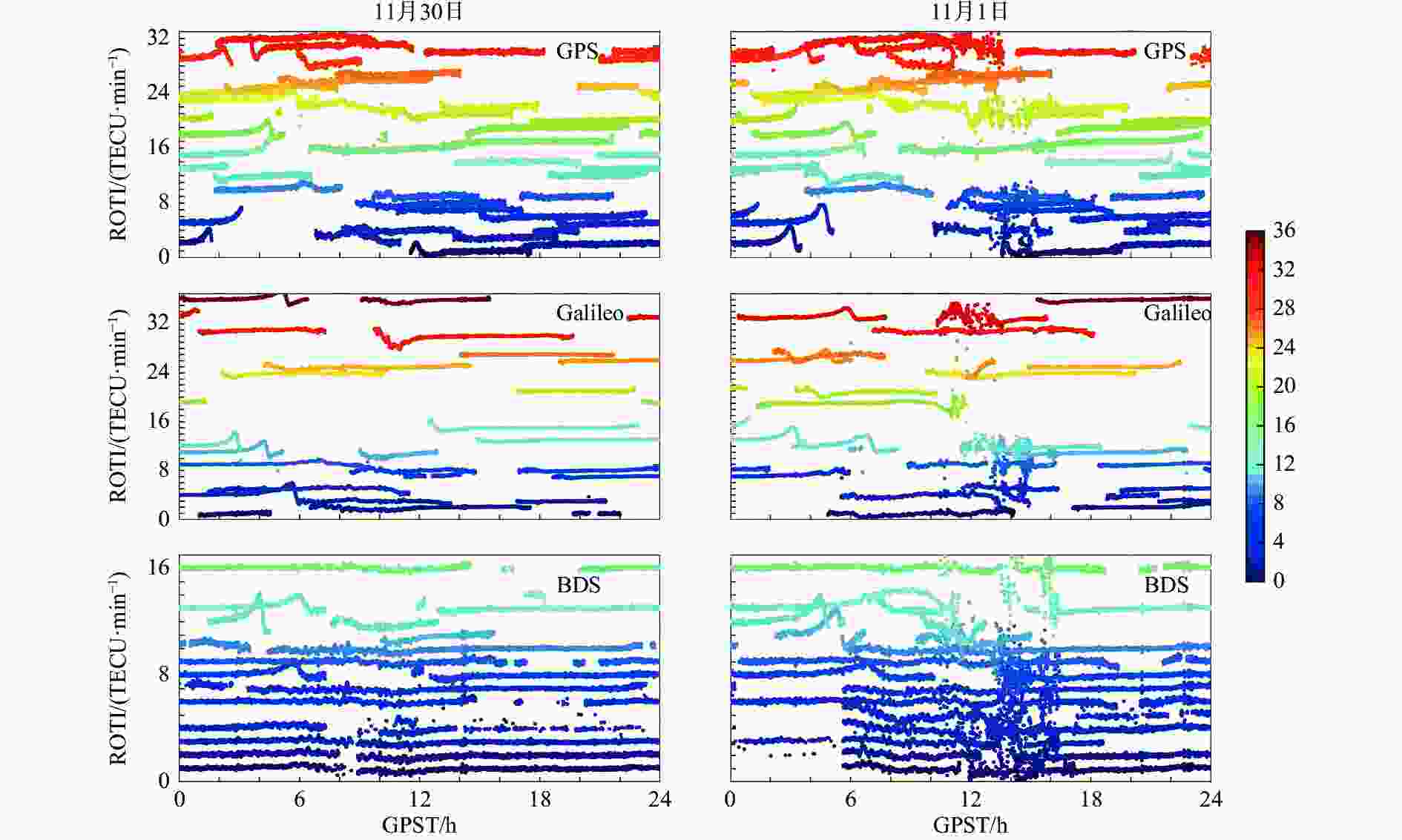
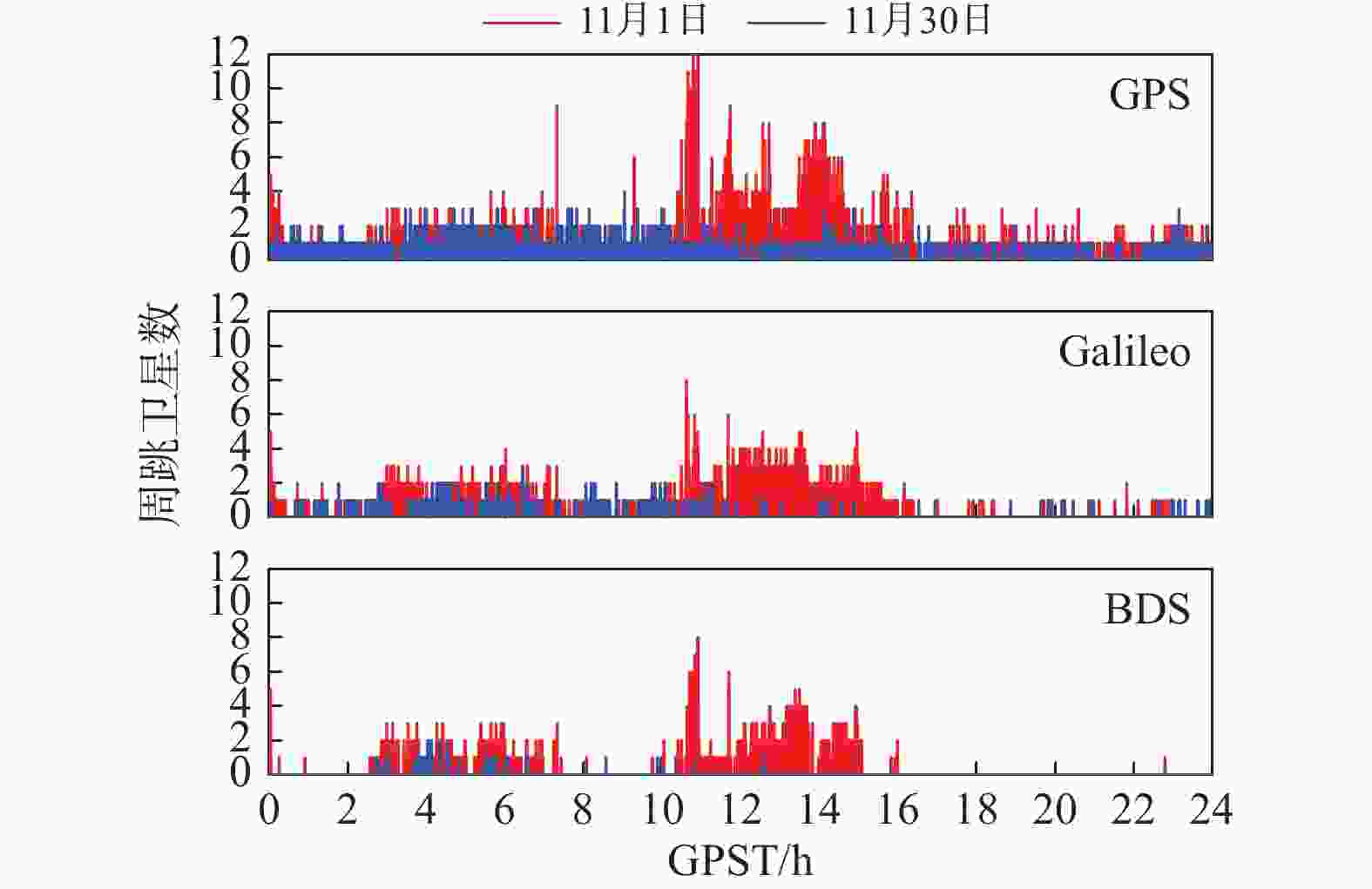
客户端:WN估计接收机钟差 WN估计,分系统、分频率分别估计ISB和IFB参数 模糊度 部分模糊度固定 表 2 2021年11月30日与11月1日发生周跳卫星总数和发生周跳历元总数
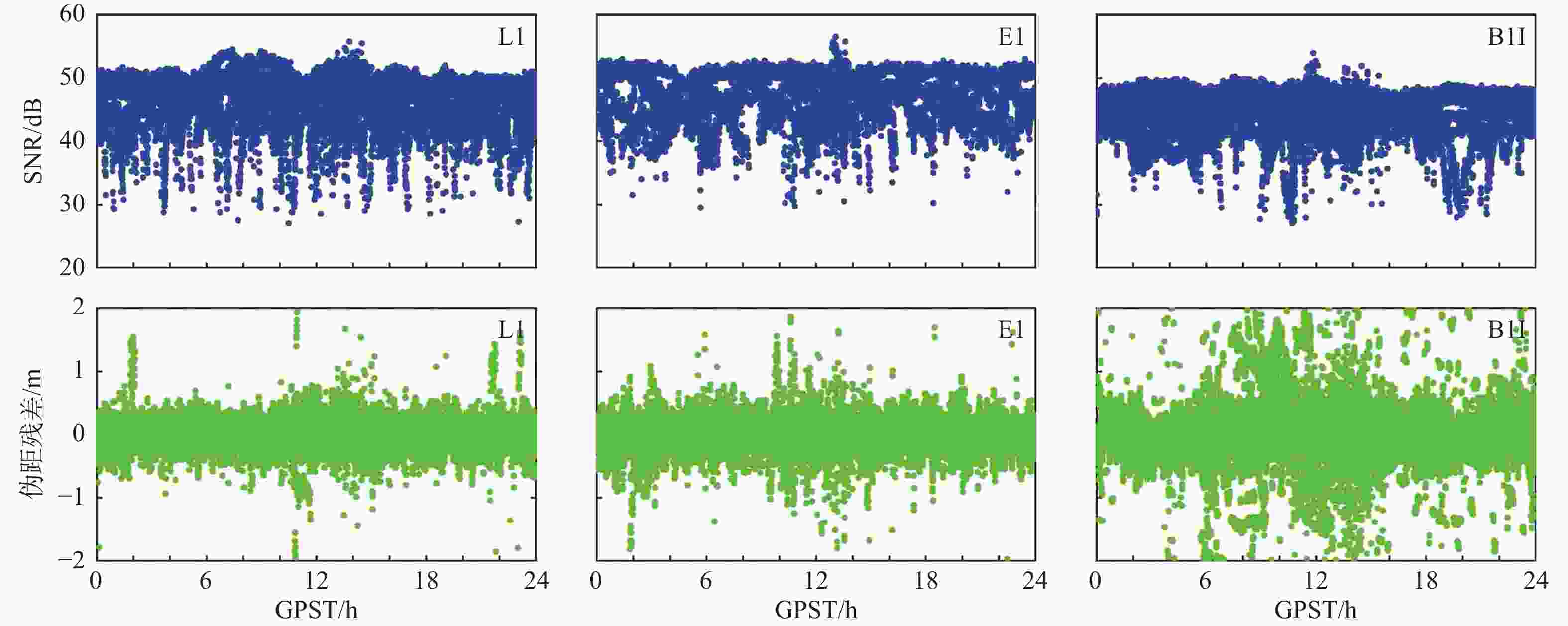
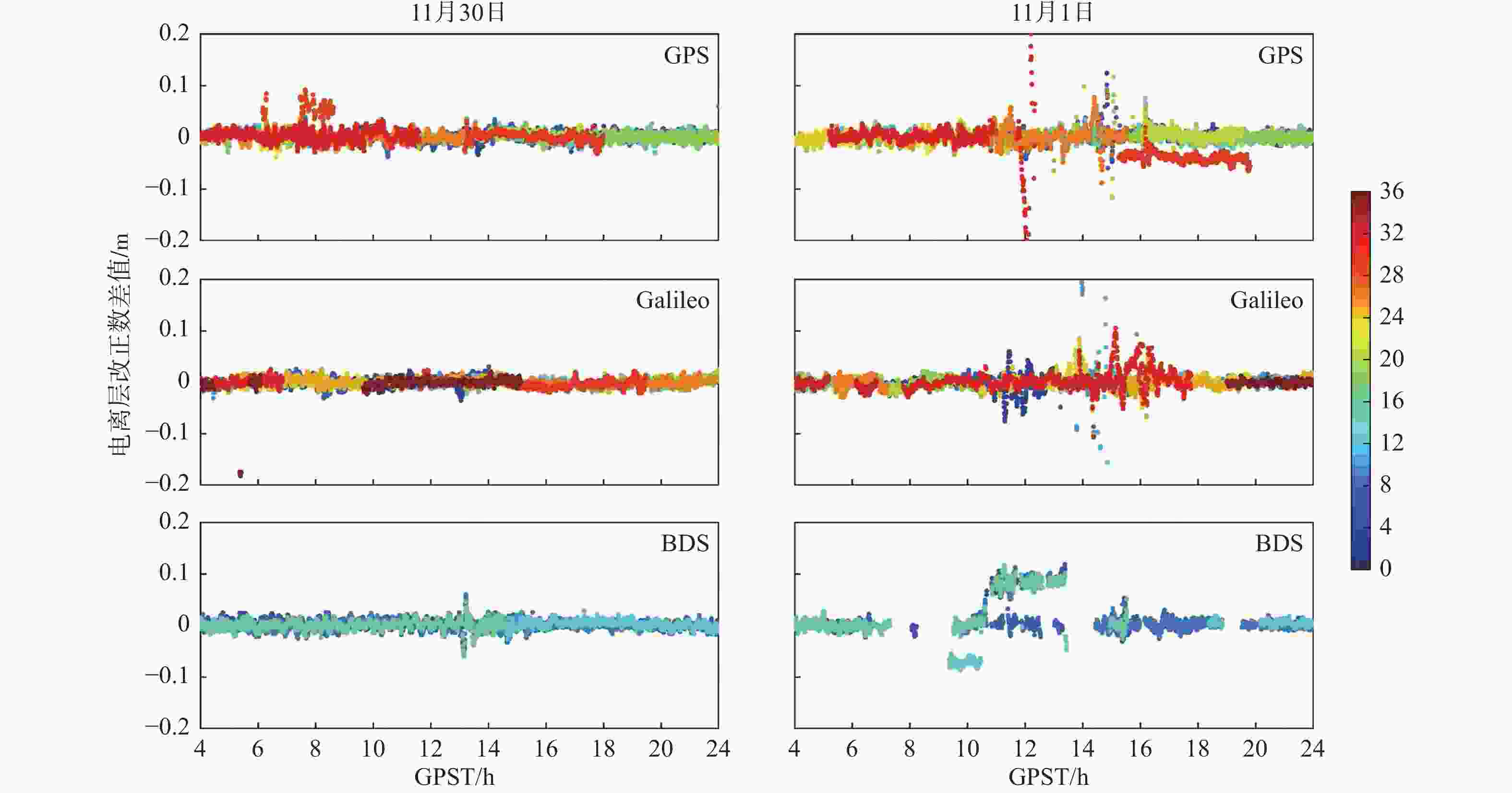
系统 发生周跳卫星总数 发生周跳历元总数 11月30日 11月1日 11月30日 11月1日 GPS 1 890 3730 1595 2 037 Galileo 538 2303 472 1304 BDS 124 1227 102 681 表 3 2021年11月30日和11月1日HKSC站电离层改正数精度与平均个数
日期 电离层改正数差值/m 改正数
平均个数GPS Galileo BDS 11月30日 0.0187 0.0111 0.0080 19.8 11月1日 0.0308 0.0182 0.0278 15.8 表 4 2021年HKSC站GPS单系统与GPS、Galileo、BDS三系统双频PPP-RTK定位统计结果
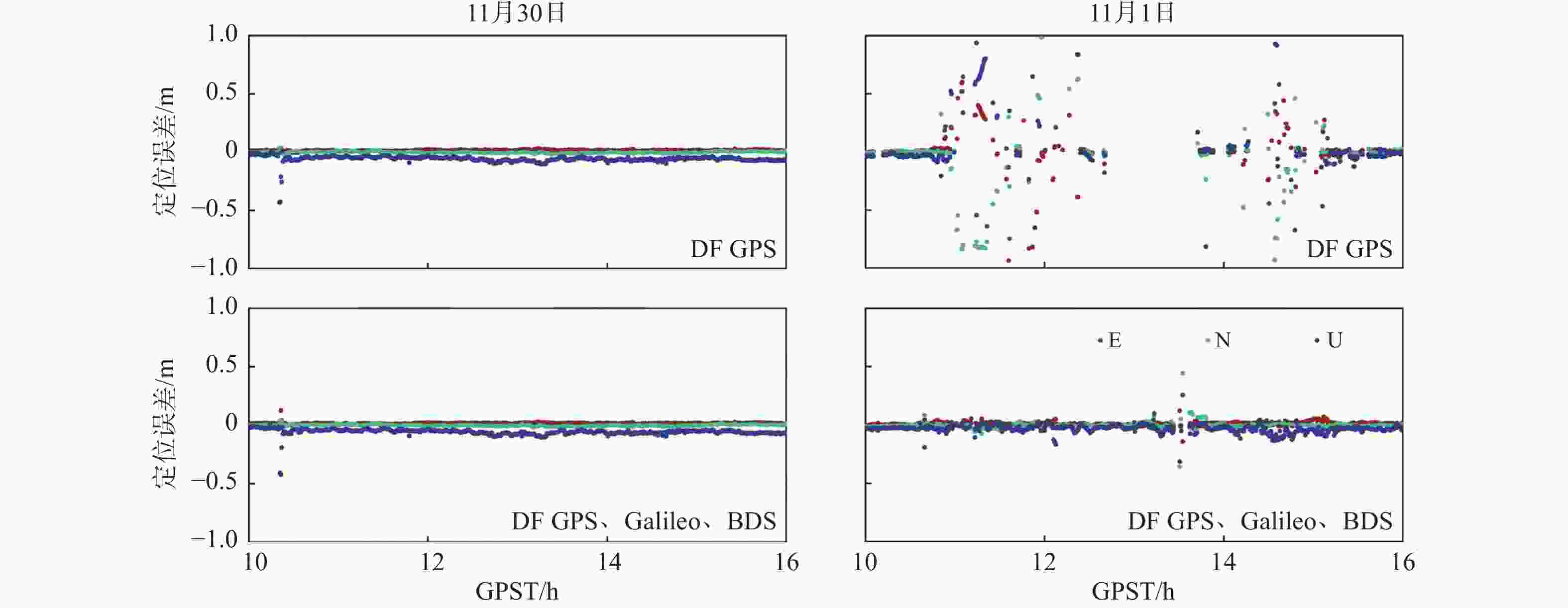
方案 时间 RMS/m 固定率/% E N U DF GPS 11月30日 0.016 0.007 0.063 100 11月1日 0.159 0.391 0.726 44.24 DF GPS、Galileo、BDS 11月30日 0.016 0.009 0.049 100 11月1日 0.020 0.028 0.047 96.12 表 5 2021年11月1日HKSC站四种方案PPP-RTK定位统计结果
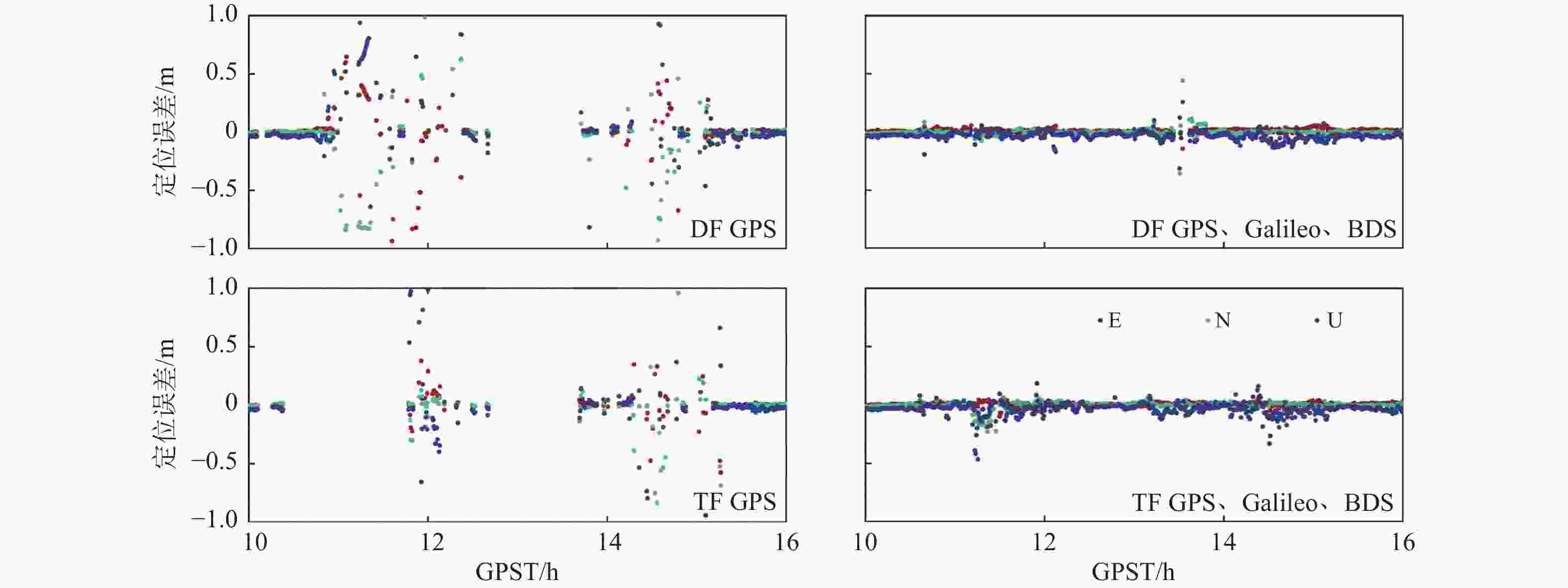
系统 频率 RMS/m 固定率/% E N U GPS DF 0.176 0.391 0.726 44.24 TF 0.133 0.143 0.793 30.51 GPS、Galileo、BDS DF 0.020 0.028 0.047 96.12 TF 0.018 0.032 0.062 97.64 -
[1] European GNSS Agency. PPP-RTK market and technology report[R]. 2019. [2] 李国主. 中国中低纬电离层闪烁监测、分析与应用研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院武汉物理与数学研究所, 2007. [3] PI X, MANNUCCI A J, LINDQWISTER U J, et al. Monitoring of global ionospheric irregularities using the worldwide GPS network[J]. Geophysical research letters, 1997, 24(18): 2283-2286. DOI: 10.1029/97GL02273 [4] XU J S, ZHU J, LI L. Effects of a major storm on GPS amplitude scintillations and phase fluctuations at wuhan in china[J]. Advances in space research, 2007, 39(8): 1318-1324. DOI: 10.1016/j.asr.2007.03.004 [5] PI X Q, MANNUCCI A J, VALANT-SPAIGHT B, et al. Observations of global and regional ionospheric irregularities and scintillation using GNSS tracking networks[J]. Proceedings of the ion pacific pnt meeting, 2013, 89(2): 752-761. [6] YANG Z, LIU Z Z. Correlation between ROTI and ionospheric scintillation indices using Hong Kong low-latitude GPS data[J]. GPS solutions, 2016, 20(4): 815-824. DOI: 10.1007/s10291-015-0492-y [7] AKALA A O, DOHERTY P H, CARRANO C S, et al. Impacts of ionospheric scintillations on GPS receivers intended for equatorial aviation applications[J]. Radio science, 2016, 47(4): 1-11. DOI: 10.1029/2012RS004995 [8] JACOBSEN K S, ANDALSVIK Y L. Overview of the 2015 st. patrick's day storm and its consequences for RTK and PPP positioning in norway[J]. Journal of space weather and space climate, 2016(6): A9. DOI: 10.1051/swsc/2016004 [9] VANI B C, FORTE B, MONICO J, et al. A novel approach to improve GNSS precise point positioning during strong ionospheric scintillation: theory and demonstration[J]. IEEE transactions on vehicular technology, 2019, 68(5): 4391-4403. DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2903988 [10] LUO X M, LOU Y D, GU S F, et al. A strategy to mitigate the ionospheric scintillation effects on BDS precise point positioning: cycle-slip threshold model[J]. Remote sensing, 2019, 11(21): 2551. DOI: 10.3390/rs11212551 [11] LI X X, GE M, DOUSA J, et al. Real-time precise point positioning regional augmentation for large GPS reference networks[J]. GPS solutions, 2014, 18(1): 61-71. DOI: 10.1007/s10291-013-0310-3 [12] LI X X, WANG B, LI X, et al. Principle and performance of multi-frequency and multi-GNSS PPP-RTK[J]. Satellite navigation, 2022, 3(1): 128-138. [13] LI X , HUANG J, LI X , et al. Multi-constellation GNSS PPP instantaneous ambiguity resolution with precise atmospheric corrections augmentation[J]. GPS solutions, 2021, 25(3). DOI:10.1007/s10291-021-01123-0 [14] KHODABANDEH A, TEUNISSEN P J G. PPP-RTK and inter-system biases: the ISB look-up table as a means to support multi-system PPP-RTK[J]. Journal of geodesy, 2016, 90(9): 837-851. DOI: 10.1007/s00190-016-0914-9 [15] GUO F, ZHANG X H, WANG J L. Timing group delay and differential code bias corrections for BeiDou positioning [J]. Journal of geodesy, 2015, 89(5): 427-445. DOI:10.1007/s00190-015-0788-2 [16] LIN P, LI X X, ZHANG X H, et al. Considering inter-frequency clock bias for BDS triple-frequency precise point positioning[J]. Remote sensing, 2017, 9(7): 734. DOI: 10.3390/rs9070734 [17] LIN P, X ZHANG X H, LI X X, et al. Characteristics of inter-frequency clock bias for block IIF satellites and its effect on triple-frequency GPS precise point positioning[J]. GPS solutions, 2017, 21(2): 811-822. DOI: 10.1007/s10291-016-0571-8 [18] BASU S, GROVES K M, BASU S, et al. Specification and forecasting of scintillations in communication/navigation links: current status and future plans[J]. Journal of atmospheric and solar-terrestrial physics, 2002, 64(16): 1745-1754. DOI: 10.1016/S1364-6826(02)00124-4 [19] WERNIK A W, ALFONSI L, MATERASSI M. Ionospheric irregularities, scintillation and its effect on systems[J]. Acta geophysica polonica, 2004, 52(2): 237-249. [20] LOUIS H E, CHARLES M M. TEQC: The multi-purpose toolkit for GPS/GLONASS data[J]. GPS solutions, 1999, 3(1): 42-49. DOI: 10.1007/PL00012778 [21] SALLES L A, VANI B C, MORAES A, et al. Investigating ionospheric scintillation effects on multifrequency GPS signals[J]. Surveys in geophysics, 2021, 42(4): 1-27. DOI: 10.1007/s10712-021-09643-7 -




 下载:
下载: